Location, Geography, Topography
- Location: Zimbabwe is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered by Zambia (northwest), Mozambique (east), South Africa (south), and Botswana (west).
- Coordinates: Lies between latitudes 15° and 23°S and longitudes 25° and 34°E.
- Topography: Dominated by high plateaus:
- Highveld (1,200–1,500 meters).
Lowveld (500–1,000 meters).
Mount Nyangani is the highest point (2,592 meters).
- Highveld (1,200–1,500 meters).
Climate Zone
- Climate Zone: Mostly tropical savanna climate, with some subtropical regions, especially in the higher elevations of the Eastern Highlands.
Capital City, Its Location, and Elevation
- Harare: Capital city located in the northeastern part of Zimbabwe.
Elevation: Approximately 1,490 meters above sea level.
Climate: Temperate due to its altitude.
Provinces and Primary Biomes
Zimbabwe has 10 provinces, each characterized by distinct biomes and ecological zones:
- Bulawayo: Urban area with semi-arid savanna.
Harare: Capital city with temperate savanna.
Manicaland: Eastern Highlands with montane forests and grasslands.
Mashonaland Central: Highveld savanna and woodland.
Mashonaland East: Miombo woodland in the Highveld and Eastern Highlands.
Mashonaland West: Miombo woodland and savanna biomes.
Masvingo: Lowveld dominated by mopane woodland.
Matabeleland North: Dry forests and Kalahari sand savanna.
Matabeleland South: Semi-arid scrubland in the Lowveld.
Midlands: Central savanna, featuring miombo woodlands.
Climate, Rainy Season, and Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: Subtropical to tropical climate with three main seasons:
- Cool, dry season: May to August.
Hot, dry season: September to mid-November.
Rainy season: Mid-November to March.
- Cool, dry season: May to August.
- Vegetation Period: The rainy season (November to March) is the main growing period for vegetation across the country.
Landscape, Biomes, and Types of Forests
- Landscape: Zimbabwe is characterized by a variety of landscapes, including rolling savannas, mountain ranges, and woodlands.
- Biomes:
- Miombo Woodlands: Common in the central and northern regions.
Mopane Woodlands: Dominates the Lowveld in the south.
Montane Forests: Found in the Eastern Highlands.
Acacia Savannas: Present in drier areas of the country.
Riverine Forests: Along major rivers, such as the Zambezi.
- Miombo Woodlands: Common in the central and northern regions.
- Forests: The country has dry forests (e.g., mopane) and wetter montane forests (Eastern Highlands).
List of All Mountain Ranges
- Eastern Highlands: A mountain range along Zimbabwe's eastern border, including:
- Mount Nyangani: The highest peak in Zimbabwe (2,592 meters).
Chimanimani Mountains: Rugged terrain with dramatic cliffs and rich biodiversity.
Vumba Mountains: Forested hills near Mutare with unique flora and fauna.
- Mount Nyangani: The highest peak in Zimbabwe (2,592 meters).
- Matobo Hills: Near Bulawayo, known for its distinctive granite boulders and ancient San rock art.
- Mavuradonha Mountains: In northern Zimbabwe, with steep slopes and miombo woodland.
List of Typical Landscape Units
- Highveld: Central plateau featuring savannas and most of the country’s population.
Lowveld: Semi-arid low-lying region in the southeast.
Kalahari Sand Region: In the west, featuring dry savannas and woodlands.
Great Dyke: A mineral-rich geological feature running through central Zimbabwe.
List of National Parks
- Hwange National Park: Largest park, home to elephants, lions, and diverse wildlife.
- Mana Pools National Park: UNESCO World Heritage Site along the Zambezi River, with hippos, crocodiles, and large mammal populations.
- Gonarezhou National Park: Part of the Greater Limpopo Transfrontier Park, featuring river valleys and savanna.
- Matobo National Park: Famous for its granite hills and ancient San rock paintings.
- Matusadona National Park: Located along Lake Kariba, known for rhinos, elephants, and scenic landscapes.
- Nyanga National Park: Situated in the Eastern Highlands, known for Zimbabwe's highest mountain and beautiful waterfalls.
- Chimanimani National Park: A mountainous area with unique flora and rich biodiversity.
- Victoria Falls National Park: Protects the Zimbabwean side of the world-famous Victoria Falls.
- Kazuma Pan National Park: Features wetlands and is known for migratory wildlife, including large herds of elephants and buffalo.
- Zambezi National Park: A rich wildlife area along the Zambezi River, near Victoria Falls.
Typical Flora and Fauna
Flora
- Miombo woodlands with Brachystegia species.
Mopane trees in the Lowveld.
Acacia trees and baobabs in dry savannas.
Montane forests in the Eastern Highlands with unique plant species, including ferns and orchids.
Fauna
- Mammals: Elephants, lions, leopards, rhinos, giraffes, buffalo, and various antelope species.
Birds: Over 670 bird species, including the African fish eagle, lilac-breasted roller, and various vultures and raptors.
Reptiles: Crocodiles, snakes (such as cobras and pythons), and lizards.
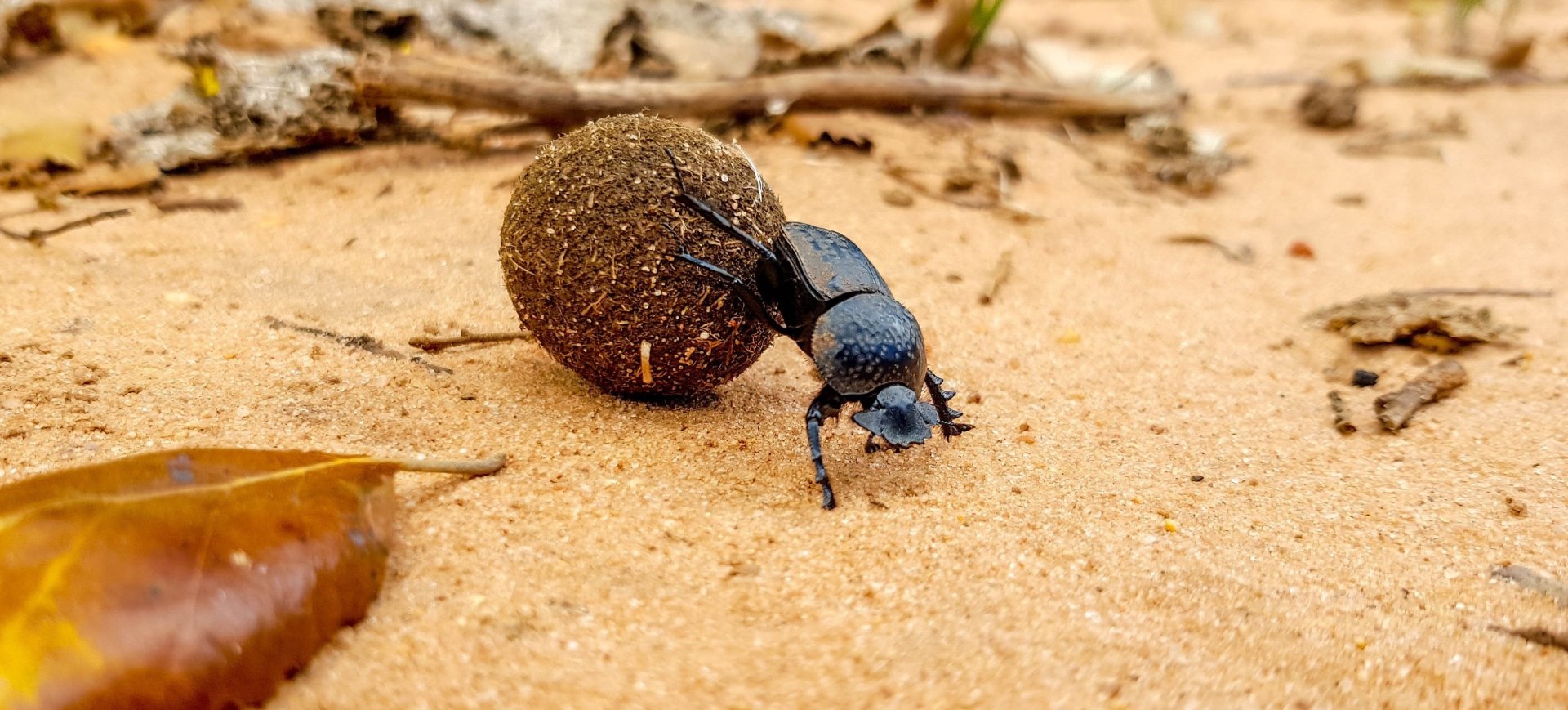
Insects: Diverse insect species, including butterflies, beetles, and termites, all playing essential ecological roles.
Our expedition in Zimbabwe