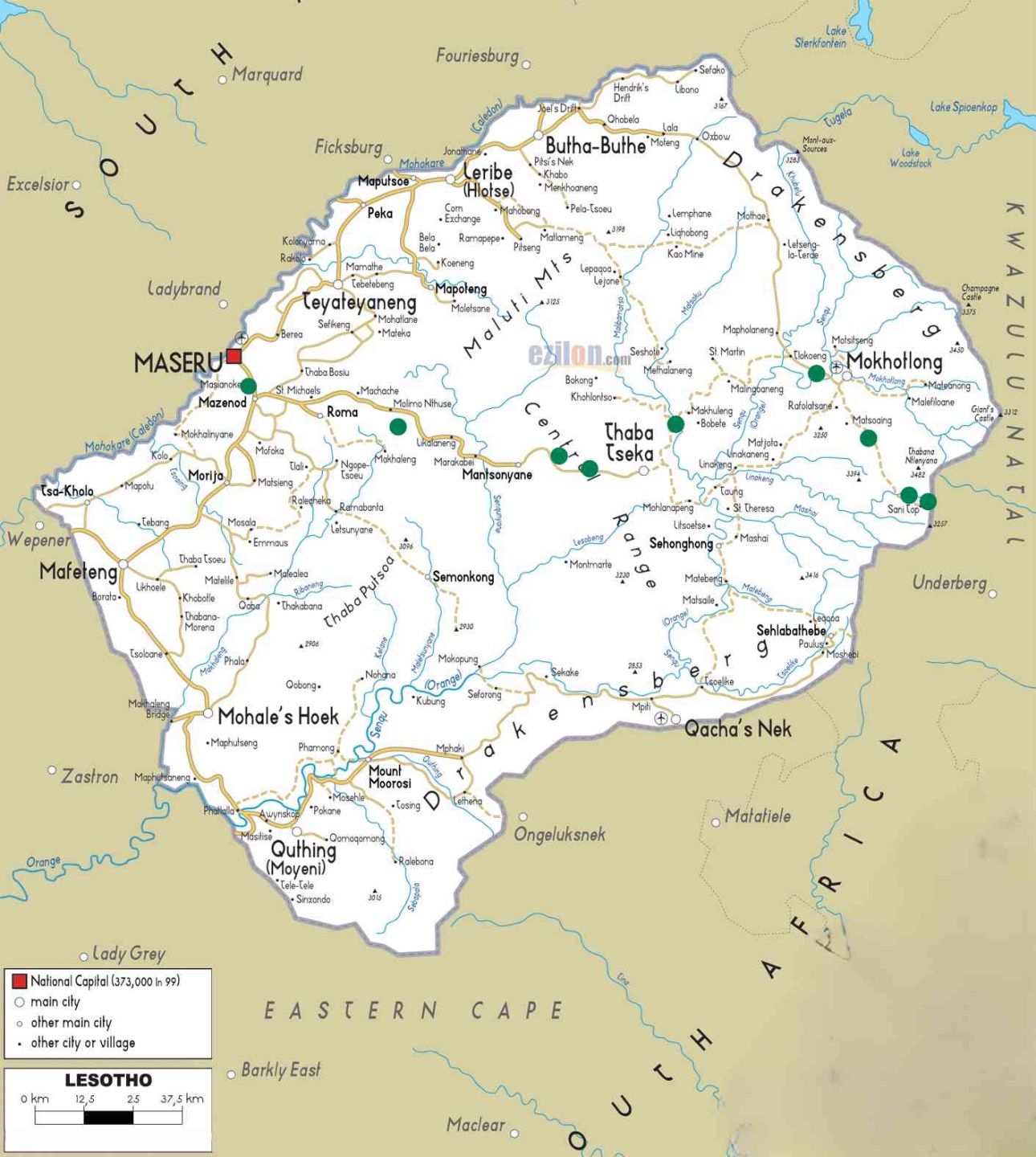
Lesotho, known as the "Kingdom in the Sky," is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. It is renowned for its stunning mountainous landscapes and unique cultural heritage.
Location and Geography
- Location: Lesotho is entirely surrounded by South Africa, situated in the southern part of the continent.
Area: Approximately 30,355 km², making it one of the smallest countries in Africa.
Topography: Lesotho is characterized by rugged mountains and high plateaus. The country has an average elevation of around 2,200 meters, making it one of the highest countries in the world.- Drakensberg Mountains: The eastern border features this prominent mountain range.
Maloti Mountains: Located in the north and west, part of the Great Escarpment.
- Drakensberg Mountains: The eastern border features this prominent mountain range.
Climate Zone
Lesotho has a temperate highland climate, which varies significantly with altitude:
- Highland Climate: Characterized by cool summers and cold winters, with snowfall in higher elevations.
- Rainfall: Most precipitation occurs during the summer months (October to March), with winter months being drier.
Capital City and Its Location
- Capital: Maseru
Location: Situated in the western part of the country, near the border with South Africa.
Elevation: Approximately 1,600 meters above sea level.
List of Districts and Their Predominant Biomes
Lesotho is divided into 10 districts, each featuring different biomes:
- Berea: Predominantly grassland and rocky outcrops.
Butha-Buthe: Highland areas with montane grasslands.
Leribe: Grasslands and scattered shrublands.
Mafeteng: Mountainous regions with agricultural areas.
Mokhotlong: High-altitude grasslands and moorlands.
Qacha's Nek: Grasslands and mountainous terrain.
Quthing: Semi-arid grasslands and mountainous areas.
Thaba-Tseka: Mountainous with a mix of grassland and shrubland.
Maseru: Urban area surrounded by grassland and hills.
Mohale's Hoek: Predominantly grassland and rocky hills.
Climate, Rainy Season, Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: Lesotho experiences four distinct seasons, with significant temperature variations between summer and winter.
- Rainy Season: The primary rainy season occurs from October to March, while the winter months (May to August) are generally dry.
- Main Vegetation Period: The growing season aligns with the rainy season, peaking from November to March.
Landscapes, Biomes, and Forest Types
- Montane Grasslands: The dominant vegetation type, with grasses and scattered shrubs.
Forests: Limited, primarily found in protected areas; include species such as Yellowwood and Wattle.
Wetlands: Occur in the higher regions, supporting unique flora and fauna.
List of Mountain Ranges
- Drakensberg Mountains: Forming the eastern boundary, these mountains are known for their dramatic cliffs and biodiversity.
Maloti Mountains: Located in the northern and western parts of the country, characterized by rugged terrain.
List of Major Landscapes
- Plateaus: The high-altitude plateau covers much of Lesotho, providing extensive grazing land.
Rivers: Numerous rivers, including the Senqu River, which is significant for water resources.
Basotho Cultural Landscape: An area showcasing traditional Basotho huts and culture.
List of National Parks
- Sehlabathebe National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its unique alpine flora and fauna.
- Maloti-Drakensberg Park: A cross-border park shared with South Africa, noted for its biodiversity and ancient rock art.
- Thaba Bosiu National Monument: A significant historical site and national park showcasing the cultural heritage of the Basotho people.
Typical Flora and Fauna of Lesotho
Flora
- Montane Vegetation: Includes species such as Erica, Protea, and various grasses adapted to high altitudes.
Alpine Plants: Found in higher elevations, including unique species such as Helichrysum and various succulents.
Forest Species: Limited areas contain trees such as Yellowwood, Hardwood, and Wattle.
Fauna
- Endemic Species: Includes the Maloti-Blue Crane and various other bird species unique to the region.
Mountain Mammals: Such as the Blesbok and Springbok, adapted to high-altitude environments.
Insects: Diverse species, including butterflies and other pollinators.
Reptiles: Including various species of lizards and snakes, adapted to mountainous habitats.
Lesotho's unique geographical and climatic conditions contribute to its rich biodiversity and cultural heritage, making it an important region for conservation and ecological studies.
Our expedition in Ethiopia