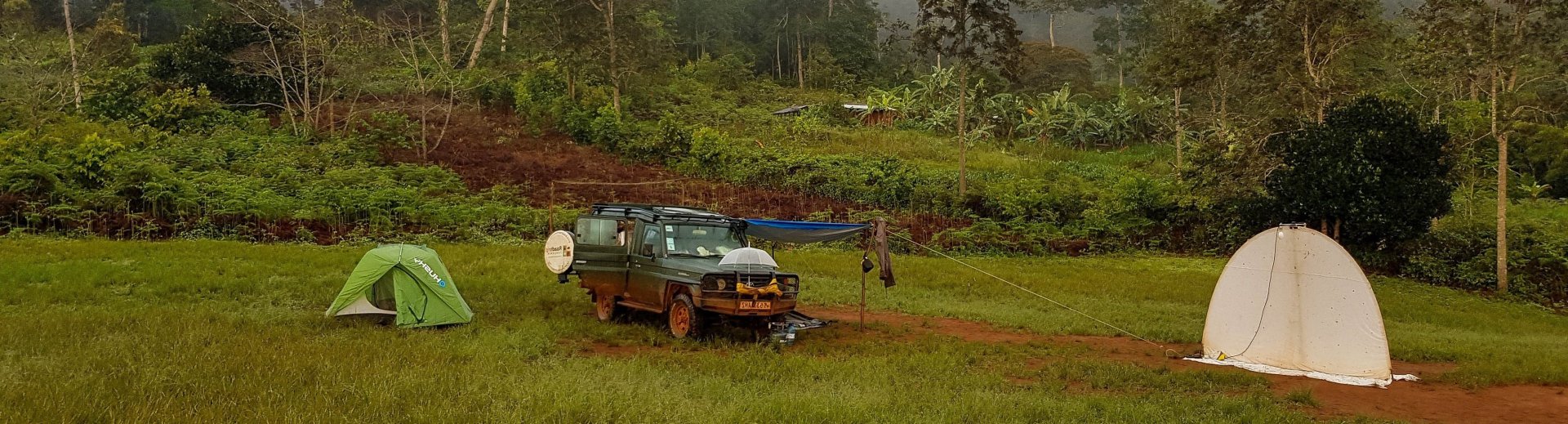
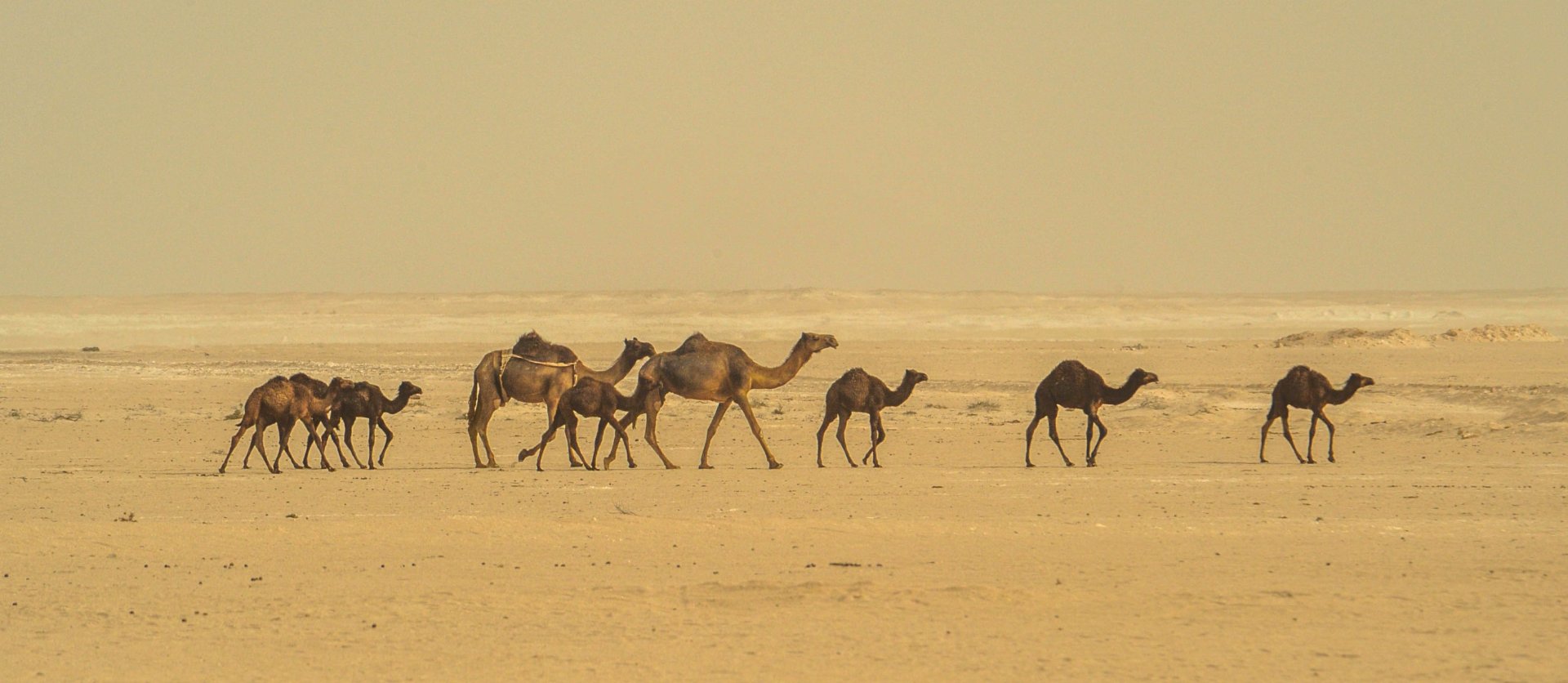
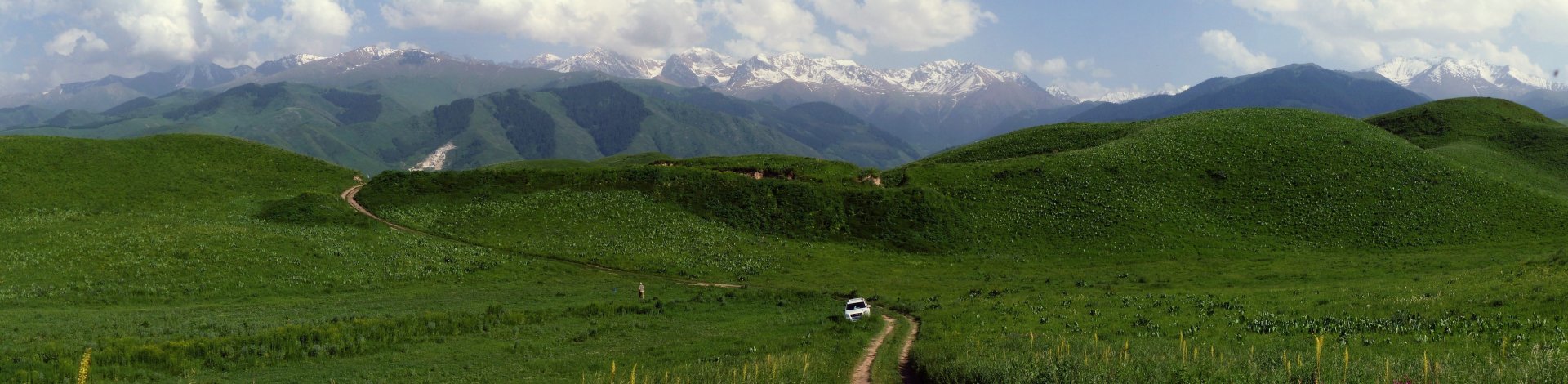
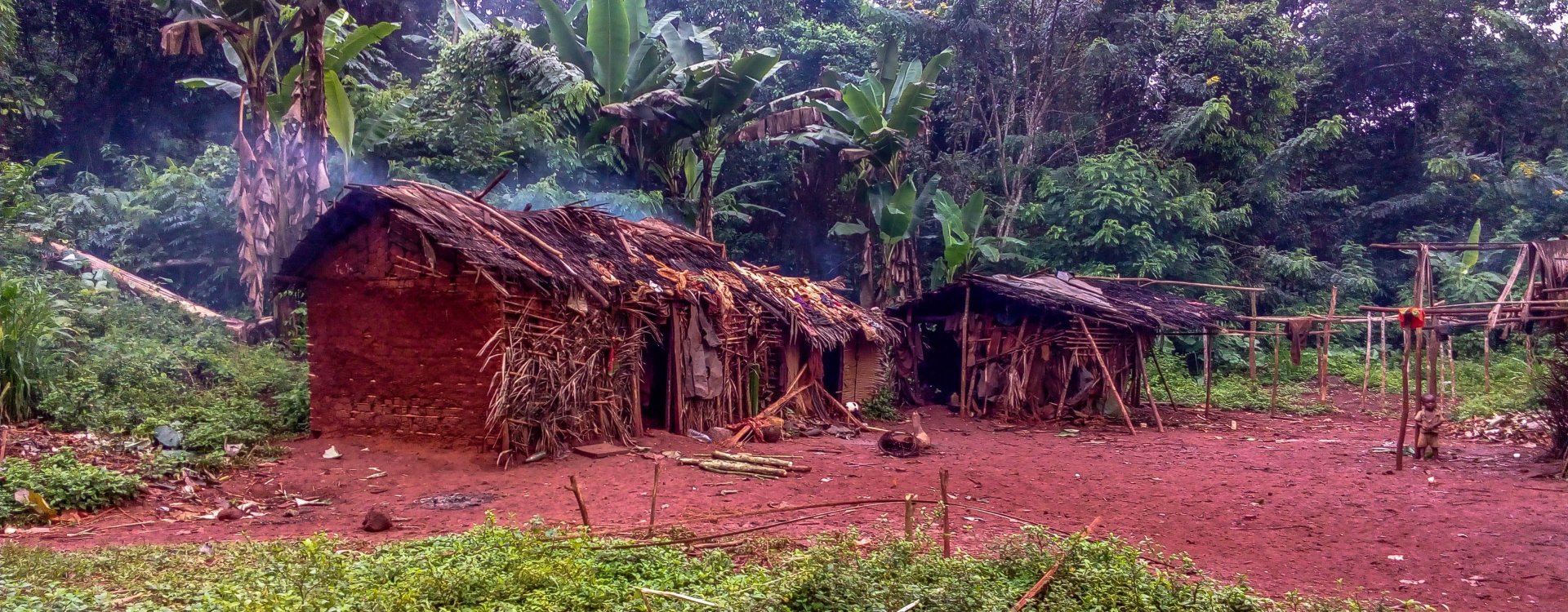
Ethiopia, located in the Horn of Africa, is known for its diverse landscapes, rich history, and unique cultural heritage. It has a variety of ecosystems ranging from high mountains to lowland deserts, making it one of the most biologically diverse countries in Africa.
Location and Geography
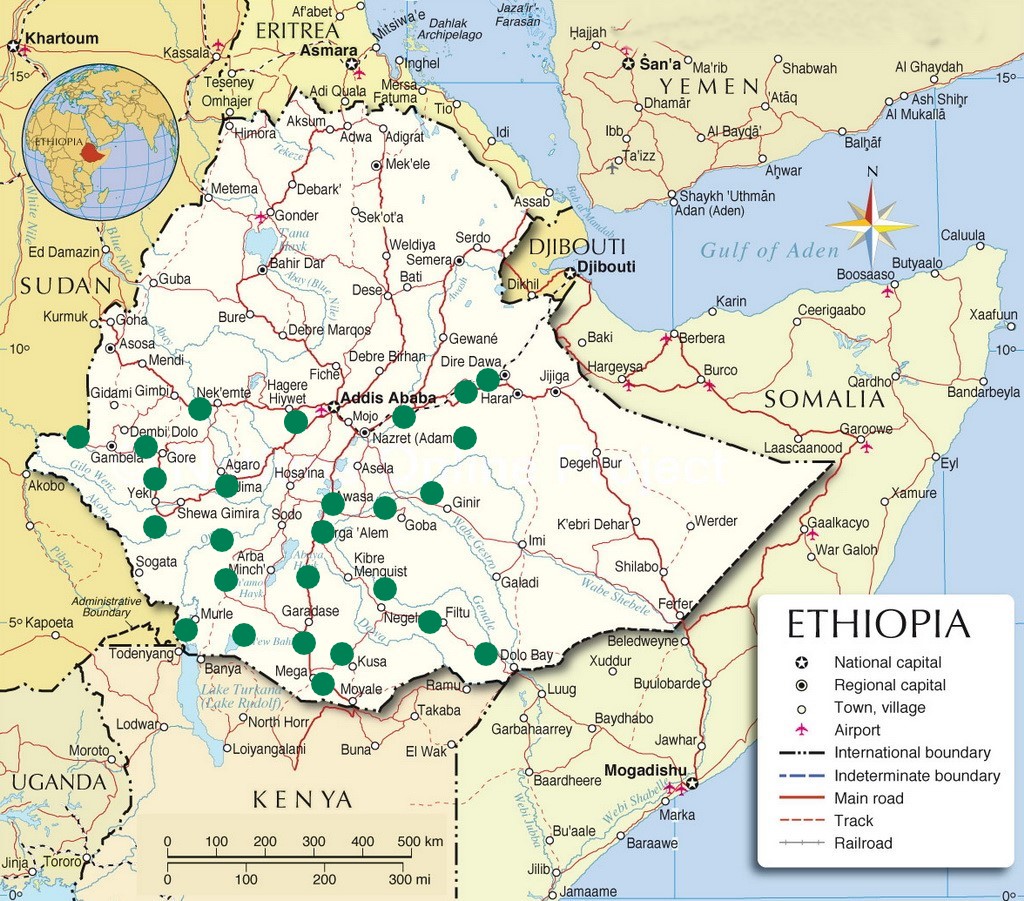
- Location: Ethiopia is a landlocked country situated in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south.
Area: Approximately 1,104,300 km², making it the second-largest country in East Africa.
Topography: The country features diverse landscapes:- Highlands: The Ethiopian Highlands, also known as the Roof of Africa, are characterized by plateaus and mountain ranges.
Great Rift Valley: A significant geological feature running through the country from north to south, with numerous lakes and volcanic formations.
Lowlands: Found in the east and southeast, characterized by arid and semi-arid conditions.
- Highlands: The Ethiopian Highlands, also known as the Roof of Africa, are characterized by plateaus and mountain ranges.
Climate Zone
Ethiopia has a varied climate due to its topography, ranging from tropical monsoon in the highlands to arid desert in the lowlands. The main climate zones include:
- Highland Climate: Cooler temperatures, with average temperatures ranging from 15°C to 20°C.
- Lowland Climate: Warmer temperatures, often exceeding 30°C, particularly in the eastern and southern regions.
- Rainfall: The main rainy season (Kiremt) occurs from June to September, while a shorter rainy season (Belg) occurs from February to May in some regions.
Capital City and Its Location
- Capital: Addis Ababa
Location: Located in the central part of the country within the Ethiopian Highlands.
Elevation: Approximately 2,355 meters above sea level, making it one of the highest capital cities in the world.
List of Regions and Their Predominant Biomes
Ethiopia is divided into 11 regions (kililoch) and two chartered cities, each with its distinct biomes:
- Addis Ababa: Urban area with surrounding highland forests.
Afar: Desert and semi-desert biomes, characterized by hot and arid conditions.
Amhara: Highland forests and grasslands, home to diverse wildlife.
Benishangul-Gumuz: Tropical rainforests and riverine ecosystems.
Dire Dawa: Mixed urban and savanna biomes.
Gambela: Wetlands and tropical rainforests.
Harari: Urban area with surrounding agricultural land and hills.
Oromia: A mix of highland and lowland ecosystems, including grasslands and forests.
Sidama: Highland and midland agricultural areas.
Somali: Arid and semi-arid savanna and desert.
Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region (SNNPR): Highland and lowland ecosystems with diverse flora and fauna.
Climate, Rainy Season, Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: Ethiopia has a diverse climate influenced by altitude, ranging from tropical in the lowlands to temperate in the highlands.
- Rainy Season: The main rainy season (Kiremt) occurs from June to September, with most rainfall concentrated during these months.
The short rainy season (Belg) occurs from February to May in certain areas, mainly in the central and southern regions. - Main Vegetation Period: Vegetation growth is highest during the rainy seasons, particularly from June to September.
Landscapes, Biomes, and Forest Types
- Tropical Rainforests: Found in the southwestern regions (Gambela) and parts of the southwest, featuring diverse flora and fauna.
Montane Forests: Predominant in the Ethiopian Highlands, these forests include species such as Juniper and Podocarpus.
Savanna and Grasslands: Dominant in the lowland areas and some regions of Oromia and the Somali region.
Desert and Semi-Desert: Characteristic of the eastern Afar region and parts of the Somali region.
List of Mountain Ranges
- Simien Mountains: Located in the northern part of the country, home to the highest peak, Ras Dashen (4,550 meters).
Bale Mountains: Located in the southeastern region, known for its unique biodiversity and endemic species.
Entoto Mountains: Surrounding Addis Ababa, characterized by hilly terrain and forests.
Western Highlands: Extending through much of western Ethiopia, characterized by high plateaus.
List of Major Landscapes
- Great Rift Valley: A significant geological feature that contains several lakes, including Lake Abaya and Lake Chamo.
Lake Tana: The largest lake in Ethiopia, situated in the northwest, and the source of the Blue Nile.
Danakil Depression: One of the hottest places on Earth, characterized by salt flats, active volcanoes, and unique geological features.
Omo Valley: Known for its rich cultural diversity and landscapes, including savanna and forested areas.
List of National Parks
- Simien Mountains National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its stunning landscapes and unique wildlife, including the Gelada baboon.
- Bale Mountains National Park: Home to endemic species such as the Ethiopian wolf and a variety of habitats, from moorlands to forests.
- Awash National Park: Known for its diverse wildlife, including oryx, gazelles, and various bird species.
- Mago National Park: Characterized by its rugged terrain and diverse flora and fauna, located near the Omo Valley.
- Omo National Park: Renowned for its rich biodiversity, including elephants, buffalo, and various bird species.
Typical Flora and Fauna of Ethiopia
Flora
- Ethiopian Highlands: Characterized by montane forests, with species such as Juniper, Podocarpus, and Hagenia.
Savanna: Includes grasses, acacia trees, and various shrubs.
Tropical Rainforest Species: Found in the southwest, featuring species like Mahogany, Teak, and various palms.
Desert Flora: Characterized by xerophytic plants such as Cacti and Succulents in arid regions.
Fauna
- Ethiopian Wolf: The rarest canid in the world, primarily found in the Bale Mountains.
Gelada Baboon: Unique to the Ethiopian Highlands, known for its distinct social structure and grazing habits.
Mountain Nyala: An endemic antelope found in the Bale Mountains.
African Elephants: Present in various national parks, particularly in Omo and Mago.
Bird Species: Ethiopia is home to over 850 species, including the Blue-winged Goose and Harlequin Duck, as well as many endemic species.
Ethiopia is a country of remarkable geographical diversity, cultural richness, and ecological significance, making it an important area for conservation and study.
Our expedition in Ethiopia