Morocco and Western Sahara encompass a rich tapestry of geography, climate, and biodiversity. Here's an overview of their location, climate, biomes, and wildlife.
Location and Geography
- Location: Morocco is located in North Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea to the west and north, respectively. Western Sahara lies to the south of Morocco and is largely a desert region, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and Algeria to the northeast.
Area: Morocco: Approximately 446,550 km² Western Sahara: Roughly 266,000 km² (disputed territory).
Topography:- Mountain Ranges: The Atlas Mountains run through central Morocco, with the Anti-Atlas to the southwest and the Rif Mountains to the north.
Deserts: Western Sahara is predominantly desert, characterized by sand dunes and arid landscapes.
- Mountain Ranges: The Atlas Mountains run through central Morocco, with the Anti-Atlas to the southwest and the Rif Mountains to the north.
Climate Zone
Morocco's climate varies by region, influenced by altitude and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean:
- Coastal Areas: Mediterranean climate with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
Inland Areas: Continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters.
Mountainous Regions: Alpine climate, with colder temperatures and snowfall in winter.
Western Sahara: Arid desert climate with very little rainfall and extreme temperature variations.
Capital City and Its Location
- Capital: Rabat
Location: Situated on the Atlantic coast, near the mouth of the Bou Regreg River.
Elevation: Approximately 80 meters above sea level.
List of Regions and Their Predominant Biomes
Morocco is divided into several regions (provinces) with varying biomes:
- Tangier-Tetouan-Al Hoceima: Mediterranean forests and coastal ecosystems.
Rif: Rugged mountainous terrain with Mediterranean vegetation.
Fes-Meknes: Semi-arid regions with a mix of forests and agricultural land.
Beni Mellal-Khenifra: Mountainous regions with mixed forests and grasslands.
Casablanca-Settat: Urban areas with agricultural land and coastal ecosystems.
Marrakech-Safi: Mix of mountains, deserts, and agriculture.
Souss-Massa: Semi-arid and desert landscapes.
Guelmim-Oued Noun: Arid desert regions with scattered vegetation.
Draa-Tafilalet: Desert landscapes with oases and mountainous areas.
Laayoune-Sakia El Hamra (Western Sahara): Predominantly desert biomes with limited vegetation.
Climate, Rainy Season, Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: Varies significantly across regions; coastal areas have a Mediterranean climate, while the interior and western Sahara experience arid conditions.
- Rainy Season: Most precipitation occurs from October to April, with the heaviest rains in winter.
- Main Vegetation Period: Growth mainly occurs during the rainy season, from November to March.
Landscapes, Biomes, and Forest Types
- Mediterranean Forests: Found in northern regions, characterized by evergreen oak and cork oak trees.
Atlas Mountains: Home to mixed forests, including cedars and pines.
Sahara Desert: Dominated by arid ecosystems, with sparse vegetation such as acacia and various desert plants.
Oases: Scattered throughout the desert, providing unique habitats for flora and fauna.
List of Mountain Ranges
- Atlas Mountains: The largest mountain range in Morocco, stretching from the Atlantic coast to the Sahara Desert.
Rif Mountains: Located in northern Morocco, near the Mediterranean Sea.
Anti-Atlas Mountains: Located to the southwest of the High Atlas, characterized by rugged terrain and dry landscapes.
Saharan Mountains: Includes small ranges in the southeastern part of Morocco and parts of Western Sahara.
List of Major Landscapes
- Sahara Desert: One of the largest deserts in the world, characterized by sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and sparse vegetation.
Oases: Fertile areas in the desert that support agriculture and unique ecosystems.
Coastal Areas: Mediterranean and Atlantic coastlines featuring beaches, wetlands, and marine life.
Highland Plateaus: Regions between the mountain ranges, used for agriculture and grazing.
List of National Parks
- Toubkal National Park: Home to North Africa’s highest peak, Mount Toubkal, and diverse flora and fauna.
- Souss-Massa National Park: Protects coastal and wetland ecosystems, as well as endangered species like the bald ibis.
- Ifrane National Park: Known for its cedar forests and diverse wildlife.
- Bouhachem Forest: A national park in the Rif Mountains, featuring rich biodiversity.
- Khenifra National Park: Encompasses parts of the Middle Atlas with forests and unique wildlife.
Typical Flora and Fauna
Flora
- Mediterranean Species: Includes cork oak, argan trees, and various shrubs.
Alpine Flora: Found in the Atlas Mountains, including edelweiss and various herbaceous plants.
Desert Vegetation: Includes acacia trees, date palms, and hardy shrubs adapted to arid conditions.
Wetland Plants: Such as reeds and various aquatic plants in coastal and oasis regions.
Fauna
- Mammals: Species such as the Barbary macaque, wild boar, and various ungulates (e.g., Barbary sheep).
Birds: Over 450 species, including the endangered bald ibis, Egyptian vulture, and various migratory birds.
Reptiles: Includes snakes and lizards adapted to desert and semi-arid environments.
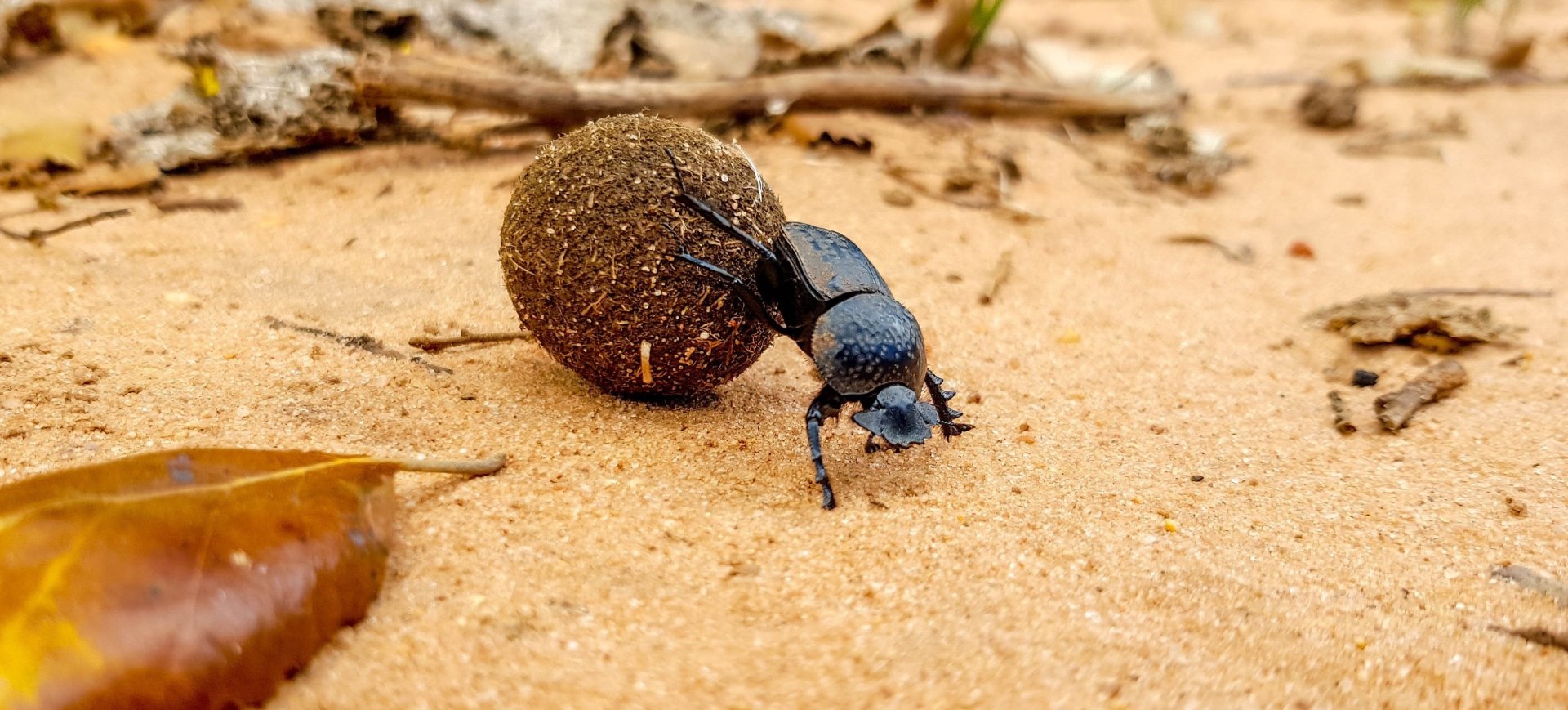
Invertebrates: Diverse species, including butterflies, beetles, and other pollinators.
Morocco and Western Sahara offer a unique blend of diverse ecosystems, rich culture, and stunning landscapes, making them significant regions for biodiversity and conservation efforts.
Our expedition in Marocco & Western Sahara