Location, Geography, Topograph
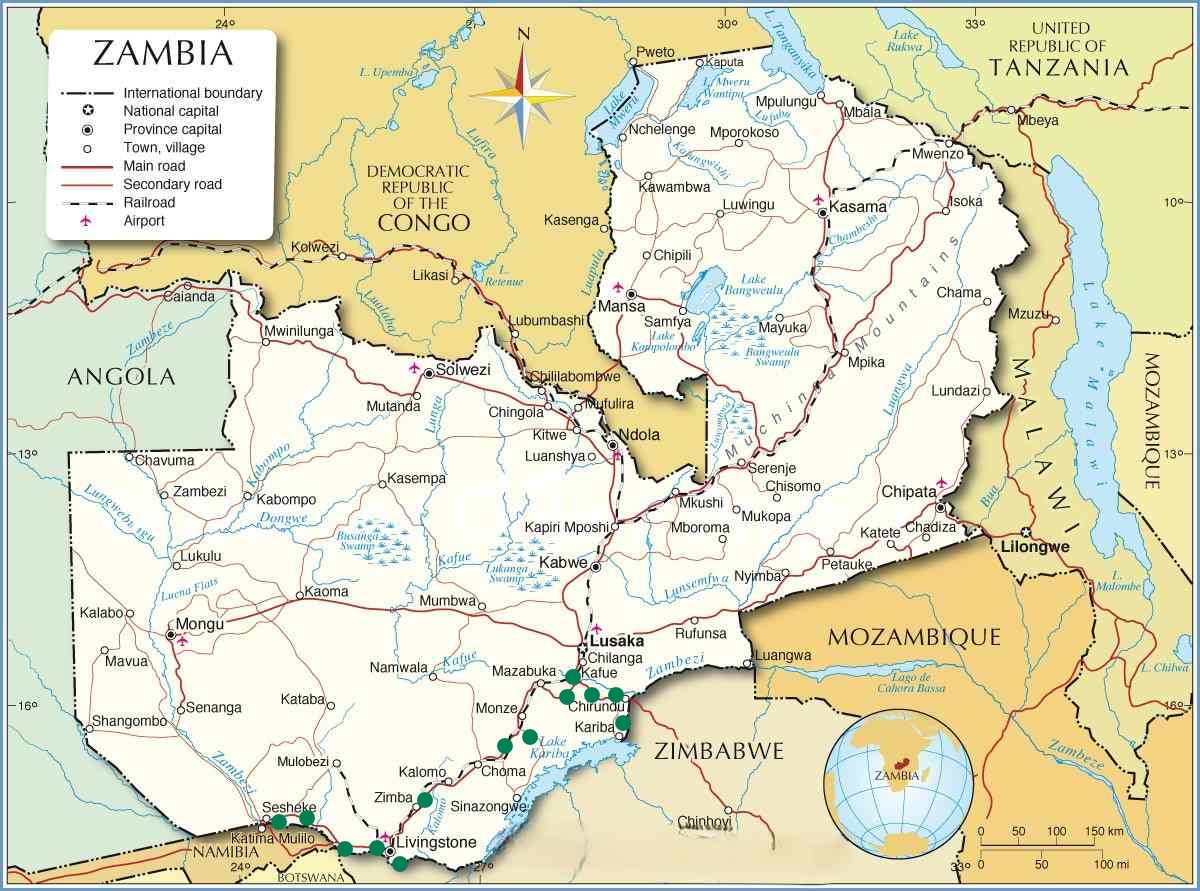
- Location: Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo (north), Tanzania (northeast), Malawi (east), Mozambique (southeast), Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia (south), and Angola (west).
- Coordinates: Located between latitudes 8° and 18°S, and longitudes 22° and 34°E.
- Topography: Zambia’s landscape is dominated by high plateaus:
- Central African Plateau: Averages between 1,000 to 1,300 meters in elevation.
Zambezi River Basin: A significant geographical feature in southern Zambia.
Muchinga Mountains: Located in the northeast.
- Central African Plateau: Averages between 1,000 to 1,300 meters in elevation.
Climate Zone
- Climate Zone: Primarily tropical savanna climate, with some regions experiencing subtropical conditions due to higher elevations, particularly in the Muchinga Highlands.
Capital City, Its Location, and Elevation
- Lusaka: The capital city located in the southern part of the central plateau.
Elevation: Approximately 1,279 meters above sea level.
Climate: Temperate climate due to its elevation, with mild winters and hot summers.
Provinces and Primary Biomes
Zambia is divided into 10 provinces, each characterized by distinct biomes and landscapes:
- Central Province: Dominated by miombo woodlands, with agricultural zones and game reserves.
Copperbelt Province: A mining-dominated area with some regions of savanna and woodland.
Eastern Province: Contains areas of plateau grasslands and miombo woodlands.
Luapula Province: Wetland ecosystems along the Luapula River and Lake Mweru.
Lusaka Province: Urban region with scattered woodlands and agricultural lands.
Muchinga Province: Dominated by mountains and highland forests in the Muchinga escarpment.
Northern Province: Features montane forests and large water bodies such as Lake Tanganyika.
North-Western Province: Extensive woodlands and rainforests, particularly near the Congo border.
Southern Province: Known for the Zambezi River valley, with mopane woodlands and grasslands.
Western Province: Features the Barotse Floodplain, with wetlands and semi-arid grasslands.
Climate, Rainy Season, and Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: Zambia experiences three distinct seasons:
- Cool, dry season: May to August.
Hot, dry season: September to November.
Rainy season: November to April, bringing most of the annual precipitation.
- Cool, dry season: May to August.
- Vegetation Period: The rainy season (November to April) is the main period for vegetation growth, particularly in agricultural zones.
Landscape, Biomes, and Types of Forests
- Landscape: Zambia is characterized by rolling plateaus, river valleys, escarpments, and wetlands.
- Biomes:
- Miombo Woodlands: Dominates much of the country, particularly the Central and Northern regions.
Mopane Woodlands: Found in drier southern regions like the Zambezi Valley.
Floodplains and Wetlands: Particularly in the Barotse Plains (Western Province) and the Bangweulu Swamps.
Montane Forests: Occur in the Muchinga Mountains and the Northern Province.
- Miombo Woodlands: Dominates much of the country, particularly the Central and Northern regions.
- Forests: Zambia has diverse woodlands (e.g., miombo, mopane) and riverine forests near large water bodies such as the Zambezi and Luangwa Rivers.
List of All Mountain Ranges
- Muchinga Mountains: Located in the northeast, forming part of the Great Rift Valley system.
Nyika Plateau: A highland region near the Malawi-Zambia border, known for grasslands and montane vegetation.
Makutu Mountains: A range in northeastern Zambia, featuring montane forests.
Zambezi Escarpment: A significant topographical feature along the Zambezi River, contributing to the dramatic landscape in the southern parts of the country.
List of Typical Landscape Units
- Zambezi River Valley: Dominating the southern regions, including the Lower Zambezi National Park and Victoria Falls area.
Barotse Floodplain: An extensive wetland system in the Western Province, subject to seasonal flooding from the Zambezi River.
Bangweulu Swamps: A vast wetland area in the north-central part of the country, home to rich biodiversity.
Kafue Flats: Floodplains along the Kafue River, rich in wildlife and significant for agriculture.
Copperbelt Plateau: Dominated by mining activities and industrial development, with patches of woodland and savanna.
List of National Parks
- Kafue National Park: One of Africa's largest parks, known for its diverse ecosystems, including wetlands, woodlands, and savannas, and wildlife like elephants, lions, and antelope.
- South Luangwa National Park: Famous for its walking safaris and large populations of leopards, hippos, and elephants.
- Lower Zambezi National Park: Located along the Zambezi River, featuring dramatic landscapes and large populations of big game like buffalo, elephants, and predators.
- Liuwa Plain National Park: Known for its wildebeest migration and vast grasslands.
- Mosi-oa-Tunya National Park: Encompassing the Zambian side of Victoria Falls, home to white rhinos and other wildlife.
- Nsumbu National Park: Situated along Lake Tanganyika, offering rich aquatic and terrestrial wildlife.
- Kasanka National Park: Famous for the annual bat migration, the largest mammal migration in the world.
- Blue Lagoon National Park: Located in the Kafue Flats, a haven for birdwatchers and aquatic species.
- Sioma Ngwezi National Park: A remote park in Western Zambia, part of the Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area, home to elephants, lions, and other large mammals.
- Isangano National Park: A park in the Northern Province known for wetlands and various species of birds and fish.
Typical Flora and Fauna
Flora
- Miombo Woodlands: Dominated by Brachystegia and Julbernardia trees.
Mopane Woodlands: Found in southern regions, particularly in the Zambezi Valley.
Riverine Forests: Along the major rivers like Zambezi and Kafue.
Montane Forests: In the higher elevations, like the Muchinga Highlands.
Wetland Vegetation: Dominates areas such as the Bangweulu Swamps and Barotse Plains.
Fauna
- Mammals: Elephants, lions, leopards, buffalo, hippos, zebras, and antelope species such as lechwe and sable antelope.
Birds: Rich birdlife, including the African fish eagle, shoebill, pelicans, and over 750 species of birds.
Reptiles: Crocodiles, various snake species (e.g., pythons, cobras), and lizards.
Insects: A wide variety of butterflies, dragonflies, and other insects, playing critical ecological roles.
Our expedition in Zambia