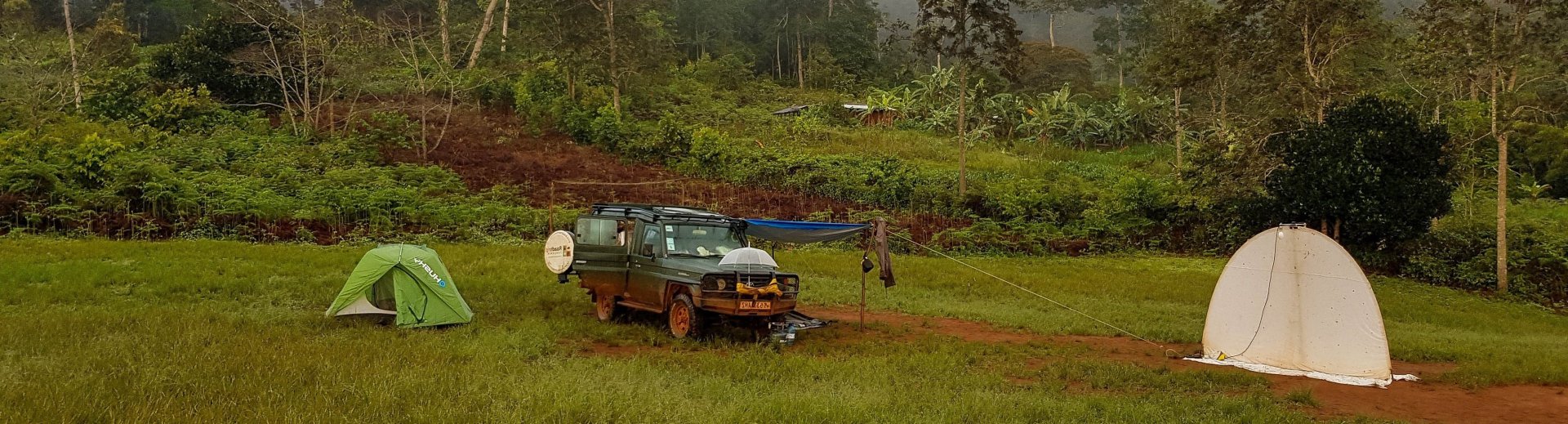
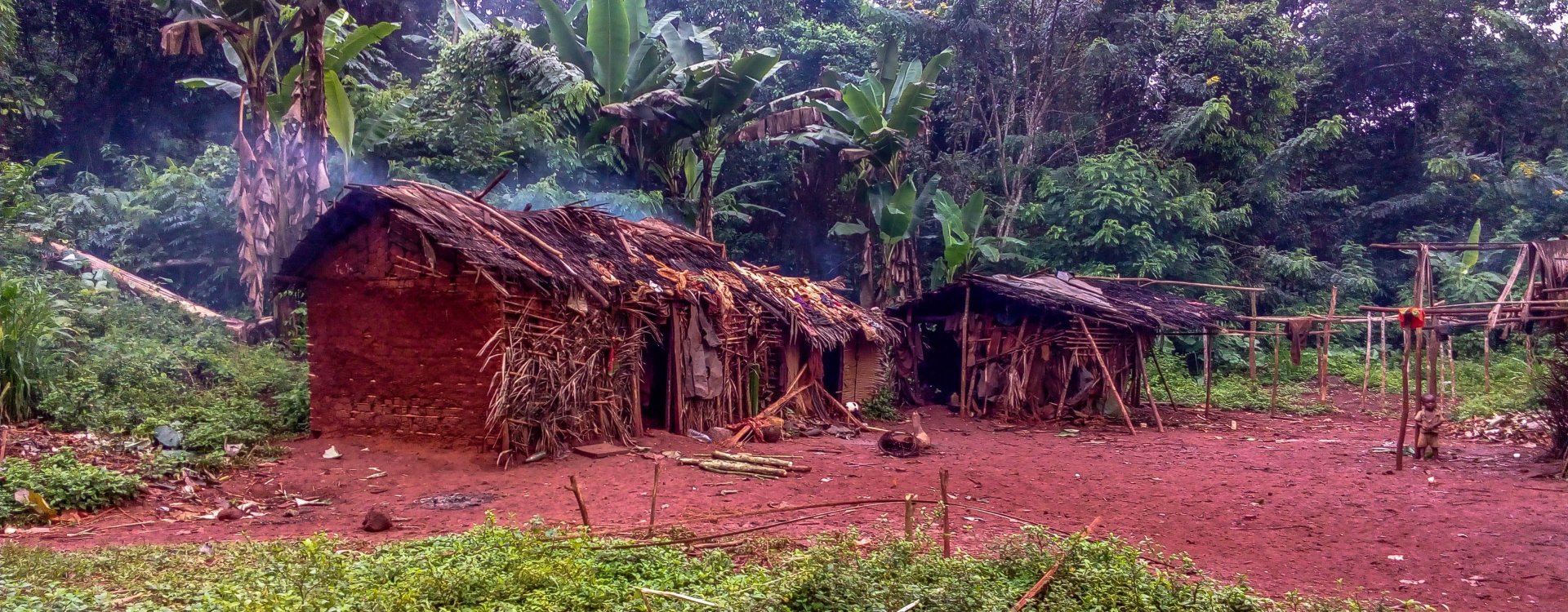
The Republic of the Congo, often referred to simply as Congo, is a country located in Central Africa. It is known for its rich natural resources, diverse ecosystems, and significant wildlife.
Location and Geography
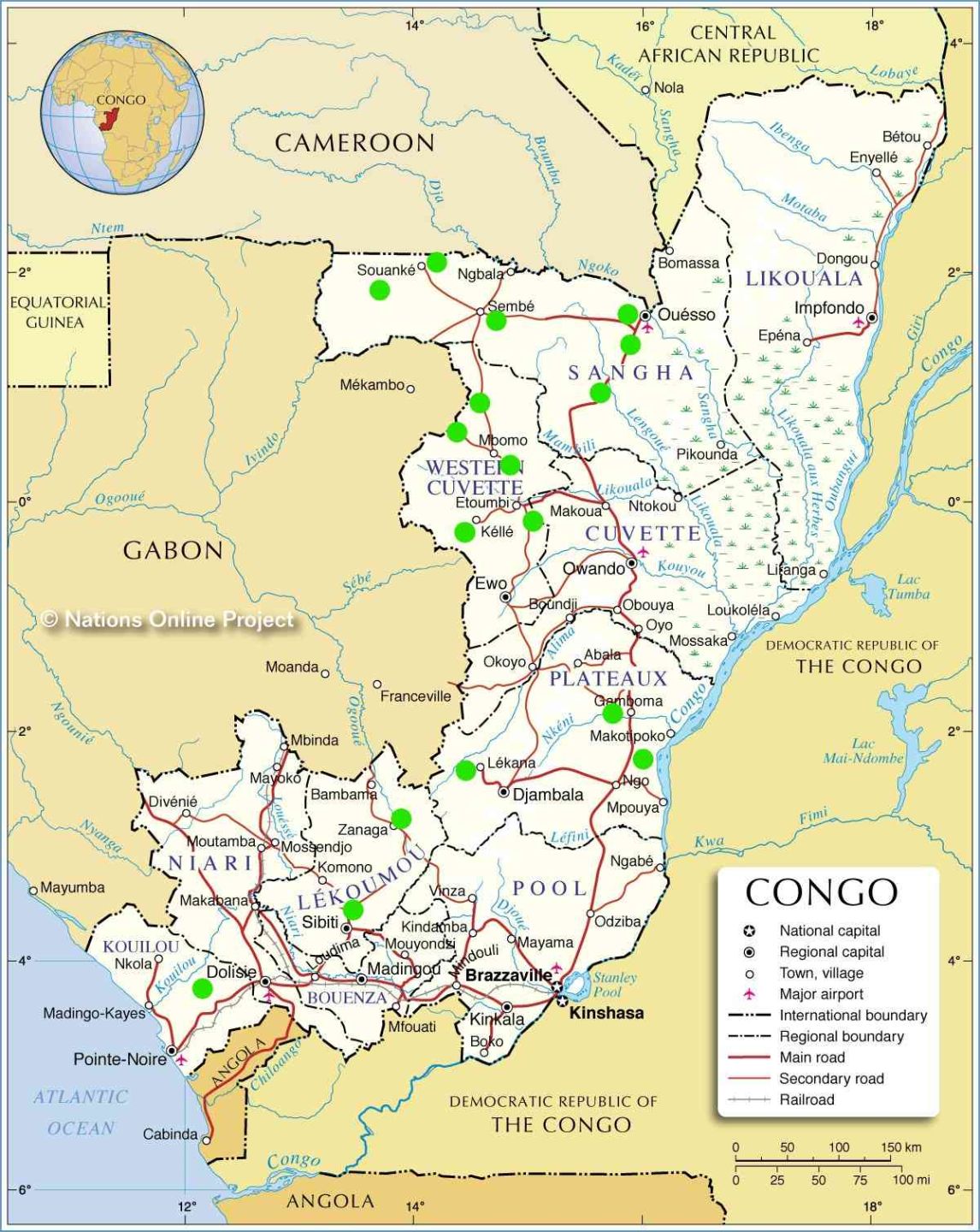
- Location: The Republic of the Congo is situated in Central Africa, bordered by Gabon to the west, Cameroon to the northwest, the Central African Republic to the north, the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the southwest.
Area: 342,000 km², making it one of the smaller countries in Africa.
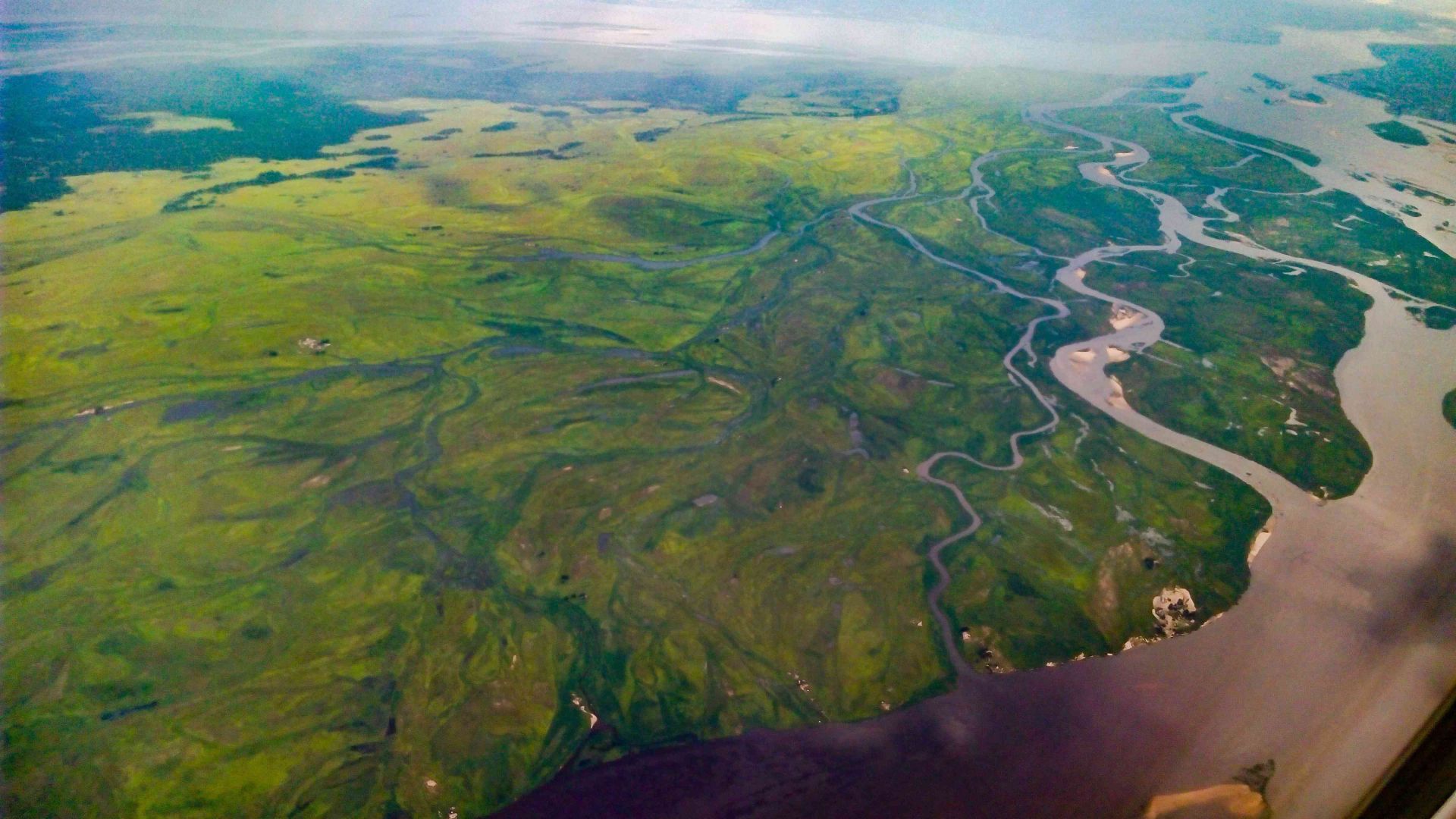
Topography: The country is characterized by a variety of geographical features:- Congo River: One of the world’s longest rivers, flowing along the southern border and serving as a vital transport route.
Plateaus: The western region features plateaus and valleys, while the eastern region is more hilly.
Mountains: The north features several mountainous areas.
- Congo River: One of the world’s longest rivers, flowing along the southern border and serving as a vital transport route.
Climate Zone
The Republic of the Congo has a tropical climate, characterized by high temperatures and humidity. It can be divided into:
- Tropical rainforest climate (Af in Köppen climate classification) in the northern regions, with dense rainforests.
- Tropical savanna climate (Aw) in the southern regions, which experience a distinct dry season.
Capital City and Its Location
- Capital: Brazzaville
Location: Situated along the Congo River, directly across from Kinshasa (the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo).
Elevation: 324 meters above sea level
List of Provinces and Their Predominant Biomes
The Republic of the Congo is divided into 12 departments, each with distinct biomes:
- Bouenza: Predominantly tropical rainforest, with some savanna.
Brazzaville: Urban areas with surrounding savanna and forest.
Cuvette: Dense tropical rainforests and wetlands.
Cuvette-Ouest: Tropical rainforests and swamp forests.
Kouilou: Coastal plains with mangroves, tropical rainforests, and savanna.
Lékoumou: Mixture of savanna and tropical rainforest.
Likouala: Dense rainforests and wetlands.
Niari: Tropical rainforest with some mountainous areas.
Plateaux: Mostly savanna and hilly terrain.
Sangha: Dense tropical rainforest and riverine ecosystems.
Sanga: Mainly tropical rainforests and wetlands
Tsuapa: Forested regions and swamps.
Climate, Rainy Season, Main Vegetation Period
- Climate: The Republic of the Congo has high humidity and temperatures averaging 25-30°C throughout the year. The climate is influenced by the presence of the Congo River and its tributaries.
- Rainy Season: The rainy season occurs from October to May, with the heaviest rains typically falling between March and May. The southern regions experience a shorter rainy season.
- Main Vegetation Period: Vegetation growth peaks during the rainy season, particularly from December to April, when conditions are most favorable for plant growth.
Landscapes, Biomes, and Forest Types
- Tropical Rainforests: These forests cover much of the northern and central regions, characterized by high biodiversity and dense vegetation.
Savanna: Found in the southern regions, consisting of grasslands with scattered trees and shrubs.
Wetlands and Swamps: Numerous wetlands, particularly around rivers, support diverse flora and fauna.
Montane Forests: Found in the northern hilly regions, these forests have distinct plant species adapted to higher altitudes.
List of Mountain Ranges
- Mayombe Mountains: Located in the southwest, near the coast, these mountains are part of the greater African Rift system.
Crystal Mountains: Located in the northern region, near the border with Gabon.
Niamou Mountains: Situated in the central part of the country.
List of Major Landscapes
- Congo River Basin: A significant geographical feature that supports a vast rainforest ecosystem.
Savanna Grasslands: Predominantly found in the southern regions, characterized by grassy plains and scattered trees.
Coastal Plains: Along the Atlantic coast, featuring mangroves and wetlands.
Plateaus: Western regions consist of plateaus interspersed with valleys.
List of National Parks
- Odzala-Kokoua National Park: A large protected area known for its biodiversity, including forest elephants and lowland gorillas.
- Conkouati-Douli National Park: Located along the coast, featuring mangroves, wetlands, and diverse wildlife.
- Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park: A UNESCO World Heritage Site rich in wildlife, including various primate species.
- Lékoumou National Park: Known for its mountainous terrain and rich biodiversity.
Typical Flora and Fauna of the Republic of the Congo
Flora
- Tropical Rainforest Species: Includes trees like Mahogany, Ebony, and various species of palms and ferns.
Savanna Species: Includes grasses, acacia trees, and shrubs.
Mangroves: Found along the coastal areas, supporting diverse marine life.
Bamboo: Common in some regions, particularly in wetlands.
Fauna
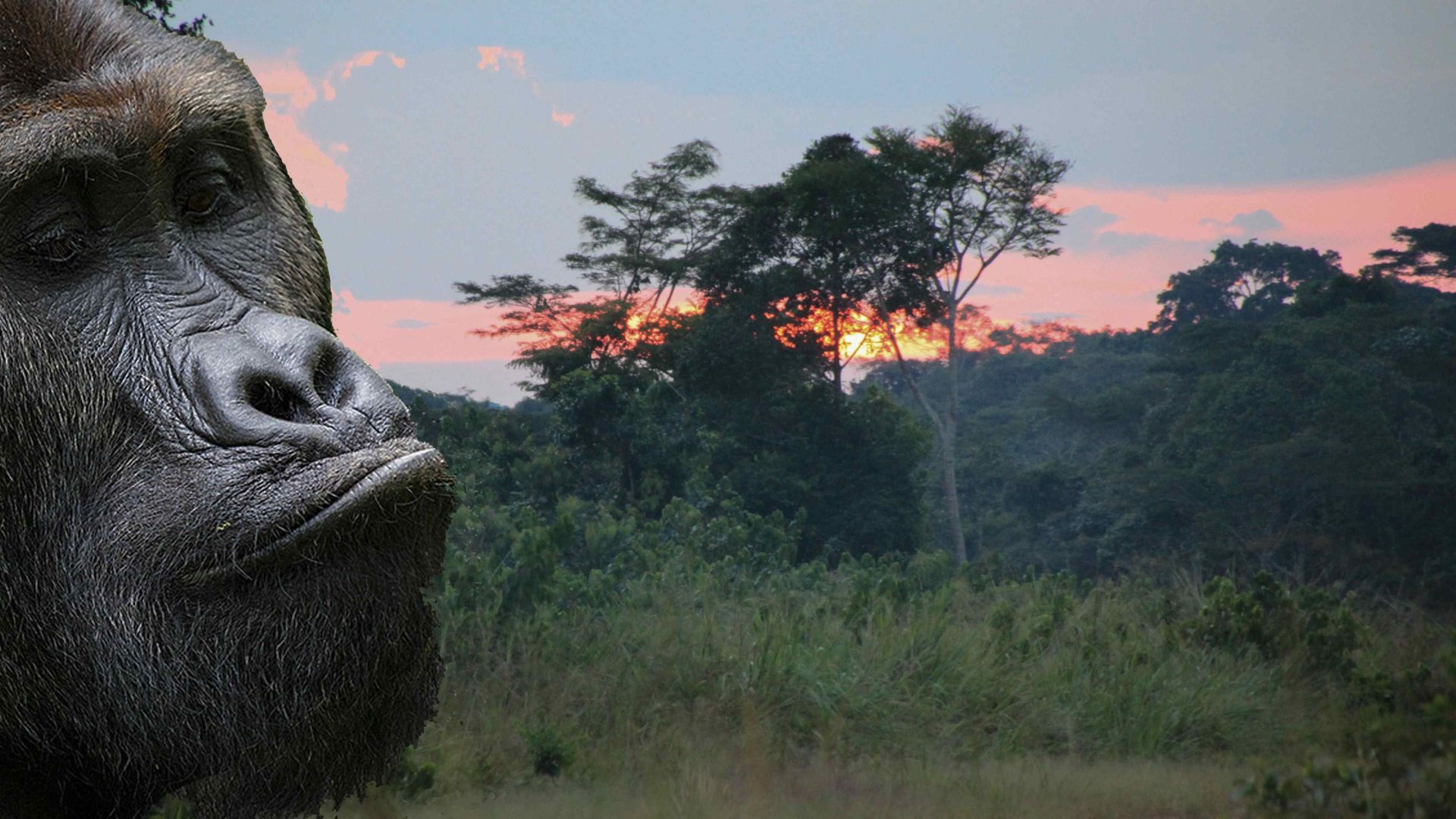
- Western Lowland Gorilla: An endangered species found in the rainforests.
Forest Elephants: Smaller and more agile than their savanna counterparts, living in dense forests.
Okapi: A unique mammal found in the rainforests, closely related to the giraffe.
Civets and Genets: Small carnivorous mammals adapted to forest life.
Various Bird Species: Including hornbills, raptors, and various colorful forest birds.
Reptiles: Such as chameleons, snakes, and various lizard species found in forests and savannas.
The Republic of the Congo is a nation of rich biodiversity, characterized by its vast rainforests, river systems, and varied ecosystems, making it a vital area for conservation and ecological research.
Our expedition in Congo